Research Areas
The UC Institute of Physics carries out both theoretical and experimental research in various areas of physics.

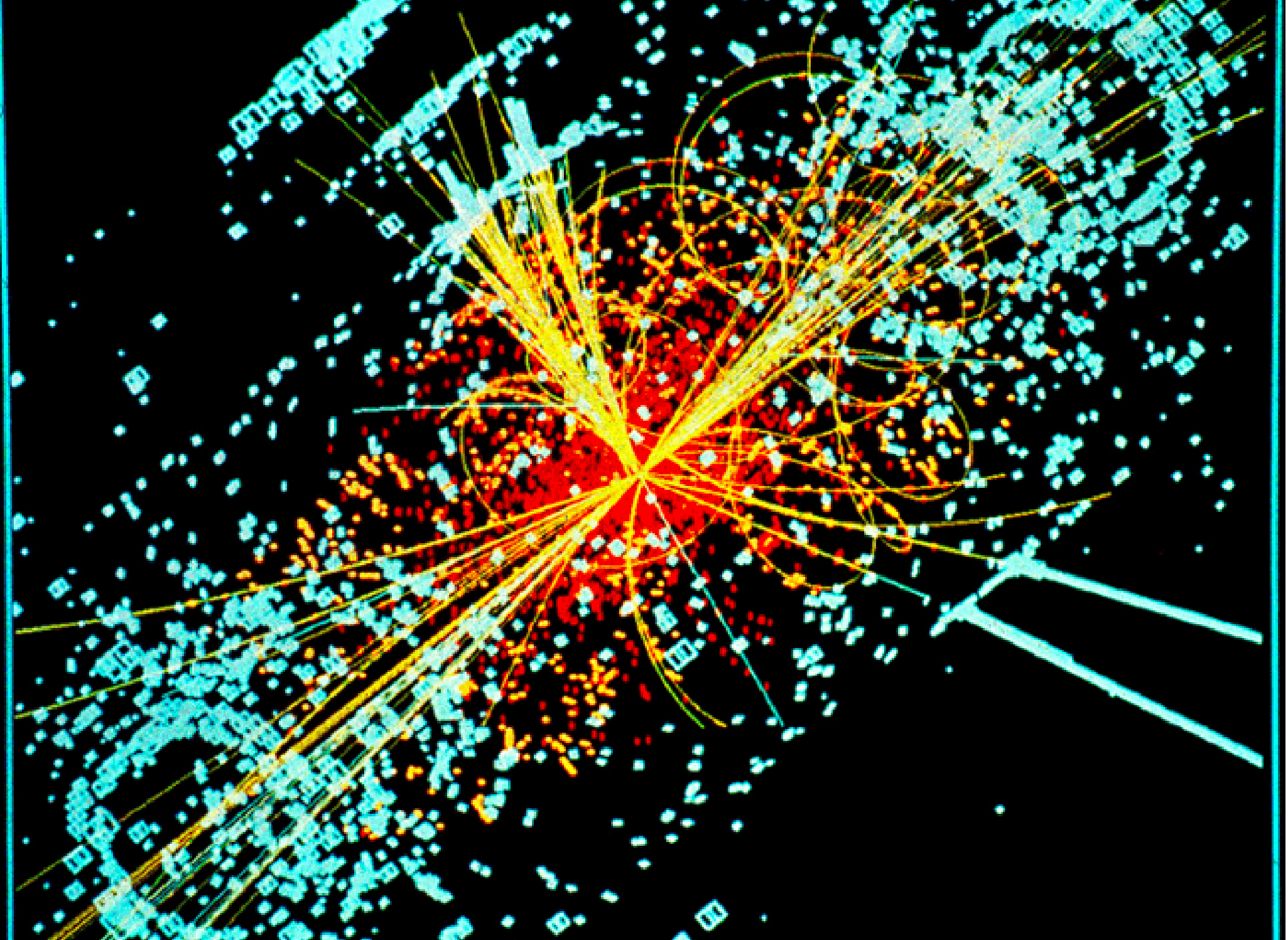
High Energy Physics
Physics is an ambitious undertaking. The fall of an apple, the behavior of electrons on a memory chip and understanding the very origin of the Universe and its evolution are part of this great human endeavor. The UC Particle Physics Group actively participates in the search for answers to many of the fundamental questions that have fascinated and captivated us for millennia.
Mathematical Physics

Since the publication of the Principia (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy) by Newton in 1685, mathematical physics has had a long tradition in the sciences. This continued with important contributions from physicists and mathematicians such as Euler, Gauss, Maxwell, Einstein, Schrödinger, Dirac, among many others.
Theoretical Condensed Matter Physics
This area of physics is concerned with studying the properties of the condensed phases of matter, particularly the solid and liquid states, following the principles of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics and, at the macroscopic level, thermodynamics. There is a direct connection between theoretical and experimental discoveries in this area of physics and the consequent technological applications, mainly in the fields of microelectronics, materials engineering and, more recently, nanotechnology. The UC Institute of Physics is a national and international benchmark in the theoretical and experimental study of condensed matter physics.

Experimental Condensed Matter Physics
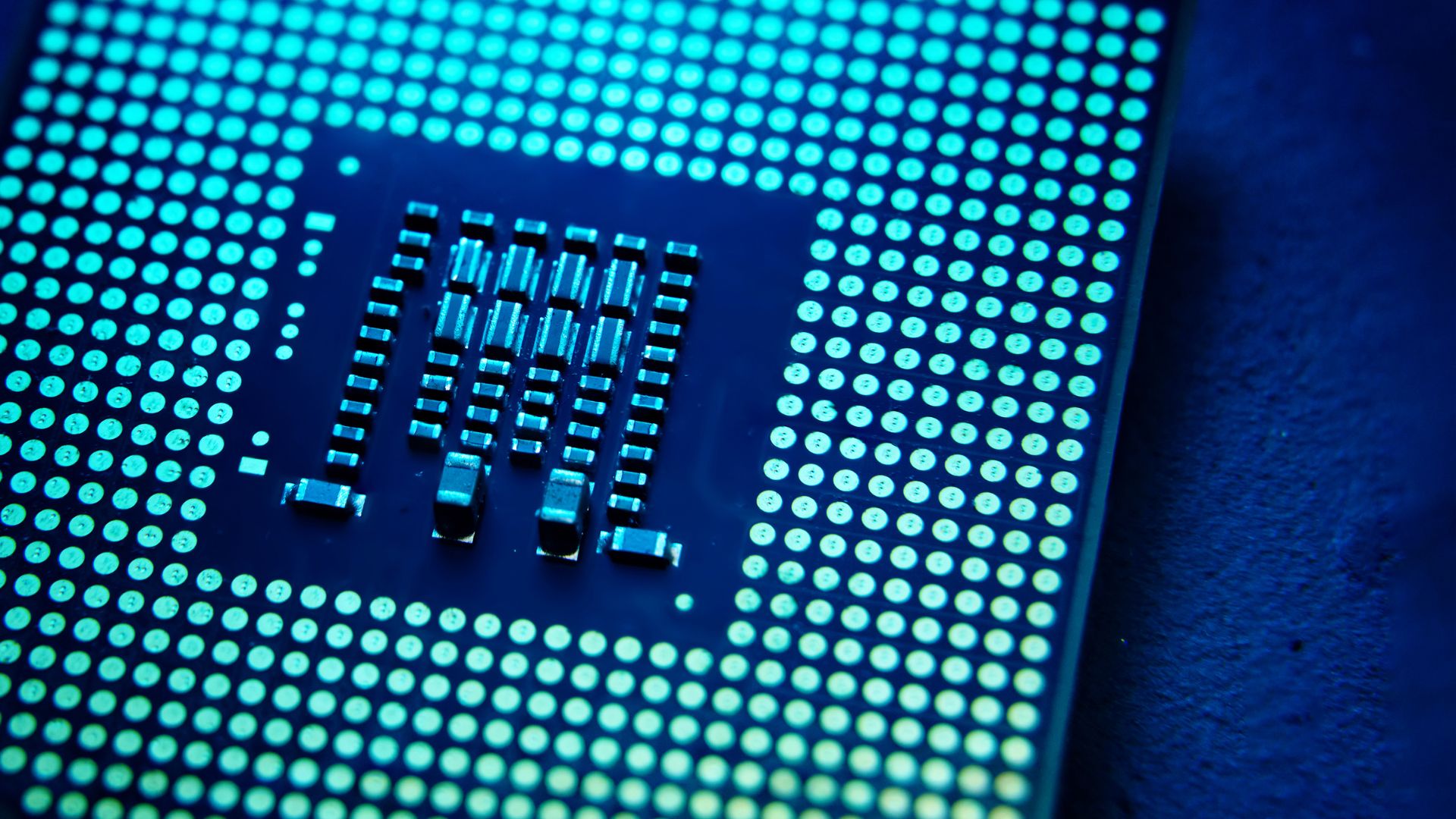
This area of physics is concerned with studying the properties of the condensed phases of matter, particularly the solid and liquid states, following the principles of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics and, at the macroscopic level, thermodynamics.
There is a direct connection between theoretical and experimental discoveries in this area of physics and the consequent technological applications, mainly in the fields of microelectronics, materials engineering and, more recently, nanotechnology.
The UC Institute of Physics is a national and international benchmark in the theoretical and experimental study of condensed matter physics.
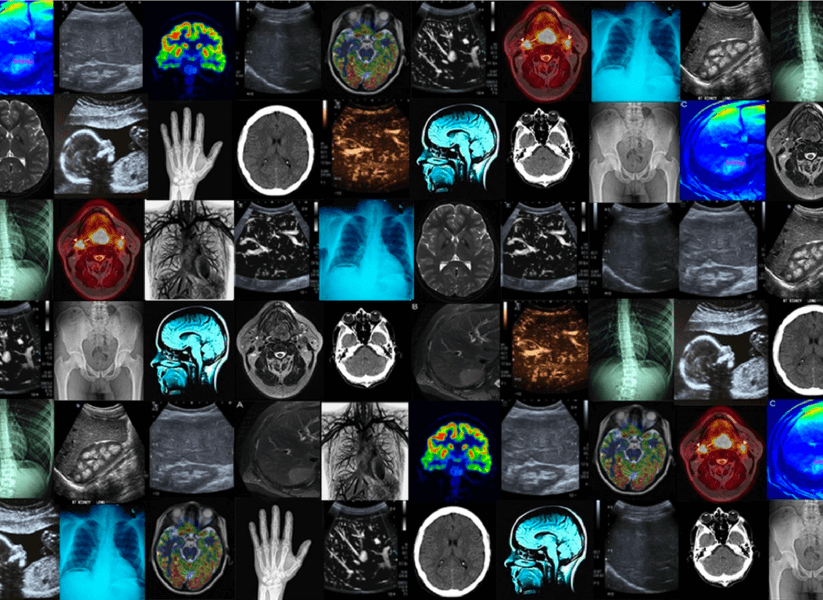
Medical Physics
Medical physics is a science consisting of the application of physics principles, concepts, methods, and techniques in medicine for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases. Since the beginning of the 20th century, and even before, it has played a fundamental role in clinical medicine as well as in biological and medical research. This area includes interesting subspecialties such as radiotherapy, diagnostic imaging, nuclear medicine, and radiation protection. In each of these, the medical physicist is heavily involved in the research, development, and implementation of new technologies and techniques. Moreover, in the clinical setting, this professional participates in the design of facilities, as well as in the purchase and quality control of equipment.
Plasma Physics

Plasma is the fourth state of matter and is present in 99% of the visible universe. We know that it is composed of ions, electrons, and neutral particles that exhibit collective behavior. Despite having charged particles, they are electrically neutral and sensitive to external electric and magnetic fields. Because plasmas correspond mainly to electrons and ions (atoms that have lost electrons), their characteristic temperatures are very high – above 10,000º C – and energy must be delivered to them to avoid recombination that ultimately results in neutral gases.
Quantum Optics
Quantum optics is the study of the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter. Currently, there are several experiments focused both on high-precision applications and on the testing of hypotheses that aim to answer fundamental questions of quantum mechanics, such as its counter-intuitive and non-local character.
